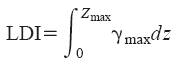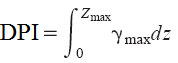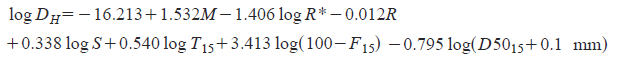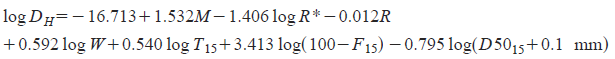Lateral Displacements
The following method of estimating the post-liquefaction lateral displacements is incorporated into NovoLiq:
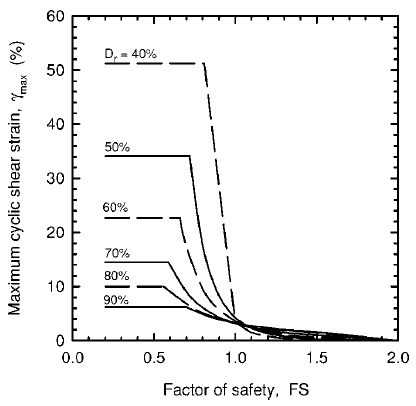
Zhang, Robertson and Brachman, 2004This method is essentially based on estimating maximum cyclic shear strain of each layer during and after liquefaction which is estimated from safety factor against soil liquefaction (FS) and relative density of soil (Dr), when Dr itself can be correlated from SPT or equivalent SPT blow counts.
Figure 1 : maximum cyclic shear strain for post liquefaction lateral displacement proposed by Zhang, Robertson and Brachman, 2004.
Then, the Lateral Displacement Index (LDI) is calculated from the following equation:
Where γmax is the maximum shear strain in each layer induced by cyclic load, and dz is depth interval at each test. Based on the topography of the site (Gently Sloped / Free Face) the lateral displacement is then estimated from LDI. The complete procedure proposed by the authors, is available in the following paper from our website:
Faris, 2006This method is similar to Zhang and Robertson method; but instead a Displacement Potential Index (DPI) is calculated based on Cyclic Stress Ratio (CSR) and N1(60)cs:
Where γmax is the maximum shear strain in each layer induced by cyclic load, and dz is depth interval at each test. Based on the topography of the site (Gently Sloped / Free Face) the lateral displacement is then estimated from DPI. The procedure is available for download from our website:
Note: Please note that for both Faris 2006 and Zhang 2004 methods, you can choose to ignore lateral spread when factor of safety is greater than a certain number. For more information please read this article. Youd 2002The following equations are used for estimation of lateral displacements:
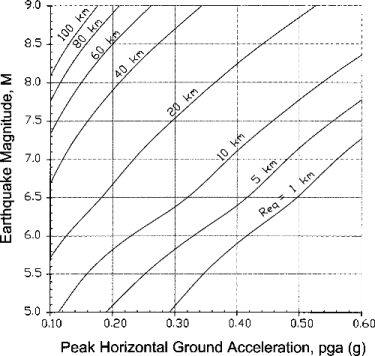
Where DH is the estimated lateral ground displacement in meters; M is the moment magnitude of the earthquake, R* is the nearest horizontal or map distance from the site to the seismic energy source in kilometers, T15 is the cumulative thickness of saturated granular layers with corrected blow counts N1(60) less than 15, in meters, F15 is the average fines content for granular materials included within T15 in percent, D5015 is the average mean grain size for granular materials within T15 in millimeters, S is the ground slope in percent, and W is the free-face ratio defined as the height of the free face divided by the distance from the base of the free face to the point in question in percent. It is recommended that R be estimated from the following graph based on PGA and M: R* = R + 10(0.89M-5.64)
The complete paper can be downloaded at:
Hamada et al 1986Hamada compiled lateral spread and borehole data from Niigata and Noshiro, Japan and developed the following preliminary empirical equation for estimating lateral spread displacement:
|